Project 6:
Electrically controlled drug delivery
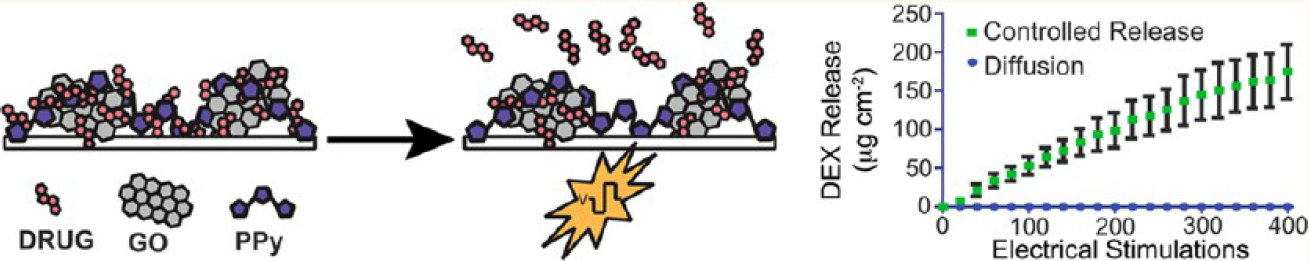
We are developing a novel electrically controlled release system that can deliver drug upon electrical command directly from the electrode sites. The electrical control allows dosing (amount and time) to be precisely defined. The delivery is based on the electroactivity of conducting polymers. The original design contains conducting polymers and the anionic dopant drug. By applying a small reductive current, the polymer loses its backbone charge and the negatively charged drug molecule is expelled. This mechanism can be further enhanced via nano-structuring and nano-materials, eg. using nano-templating to create a nanoporous film, nano-layering to create sponge-like actuated drug release and incorporating multiwall carbon nanotubes (CNT) as drug reservoirs or graphene oxide nanosheets as drug carrier. PEDOT/CNT film loaded with anti-inflammatory dexamethasone has been applied on neural electrodes, and the electrically stimulated drug release improves neuronal survival around the electrodes. When coupled with a real time biosensor that detects biomarkers of diseases (inflammation, degeneration, oxidative stress), on-demand delivery of therapeutics may be achieved. When combined with neural electrode arrays, the technology can focally modulate the local neural network. In addition to being a great enabling technology for neuroscience research, further development of the technology may have therapeutic applications in the diagnosis and treatment of neurological diseases or injuries. One active project aims at combined delivery of neurochemical and electrical cues as a therapy for treating muscle atrophy post peripheral nerve injury (funded by ARMY).
Example publications include:
- Reecha Wadhwa, Carl F. Lagenaur and Xinyan Tracy Cui, Electrochemically controlled release of dexamethasone from conducting polymer polypyrrole coated electrode, Journal of Controlled Release, Volume 110, Issue 3, 21 February 2006, Pages 531-541
- Luo, X., C. Matranga, S. Tan, N. Alba, and X. T. Cui, Carbon nanotube nanoreservior for controlled release of anti-inflammatory dexamethasone. Biomaterials, 2011. 32(26): p. 6316-6323.
- Stauffer, W. R., P. M. Lau, G. Q. Bi, and X. T. Cui, Rapid modulation of local neural activity by controlled drug release from polymer-coated recording microelectrodes. J Neural Eng, 2011.8(4): p. 044001.
- C. L. Weaver, J. M. Larosa, X. Luo, and X. T. Cui, Electrically controlled drug delivery from graphene oxide nanocomposite films. ACS Nano, 2014. 8(2): p. 1834-43
- Kolarcik, Christi; Catt, Kasey; Rost, Erika; Albrecht, Ingrid; Bourbeau, Dennis; Du, Zhanhong; Kozai, Takashi; Luo, Xiliang; Weber, Doug; Cui, X. Tracy, Evaluation of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) /carbon nanotube neural electrode coatings for stimulation in the dorsal root ganglion, accepted by Journal of Neural Engineering,